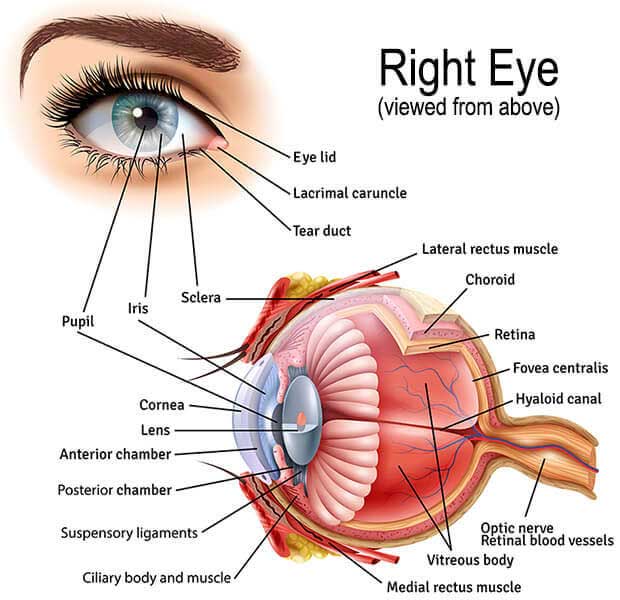
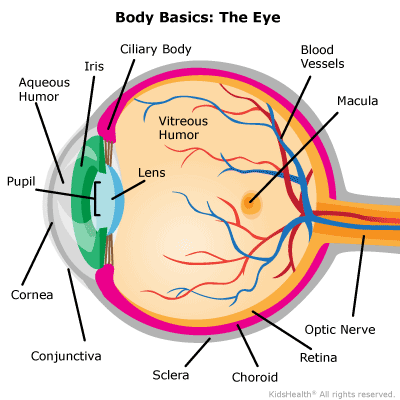
Keep an Eye on your Eyes
By:NIH News In Health
The eyes are more than windows to the soul. With advances in eye health technology, they can also give a unique look into your health.The eyes are more than windows to the soul. With advances in eye health technology, they can also give a unique look into your health. "The eye is a real window into what's happening in your body," says NIH eye health expert Dr. Houmam Araj. It's a convenient way for a doctor to get a clear view of your blood vessels, ne rves, and connecting tissue without surgery. Researchers are working on new technologies to help doctors get a better look into the eye and catch diseases earlier. They're also designing new tools to help people w ith vision loss get around in their daily lives. What Doctors See Now Getting regular eye exams is important, even if you think your vision is fine. Eye exams allow an eye care professional to monitor your eyes for common vision problems and signs of disease. "There aren't early warning signs for the most common eye diseases," says NIH eye specialist Dr. Rachel Bishop. "By identifying diseases early, you have the best treatment options and the best chance of preserving good vision."
As you can see by this article, it is very very important to take care of your eyes, and if you are struggling seek help, don't wait.